🦷 How to Treat a Dental Cyst?

What Exactly is a Dental Cyst?
A dental cyst is a sack of fluid within the jawbone or soft tissue, like the gums, usually around the roots of your tooth. Often, these cysts develop after infections, impactions, or other dental issues. Even though they are not cancerous, the cysts can become very painful and cause damage to adjacent teeth and surrounding tissues if untreated. First and foremost, we need to know what these cysts are for effective management and treatment.
Dental Cyst Signs
In the initial stages, most dental cysts do not manifest any symptoms that an individual can easily notice; however, they can lead to swelling, pain, or infection if they are neglected. Some common symptoms are:
- Swelling or pain in the affected area
- Uncomfortable or painful feeling when biting or chewing
- A lump, or a bump, that is palpable in the gums or jawbone
- A tooth may become loose in the presence of a cyst if it affects the root
- Halitosis or a lousy taste in the mouth, particularly if there is a possibility that the cyst got infected
If you observe any of these symptoms, it is crucial that you visit a dentist immediately and not let things get out of hand.
How Dental Cysts Are Treated?
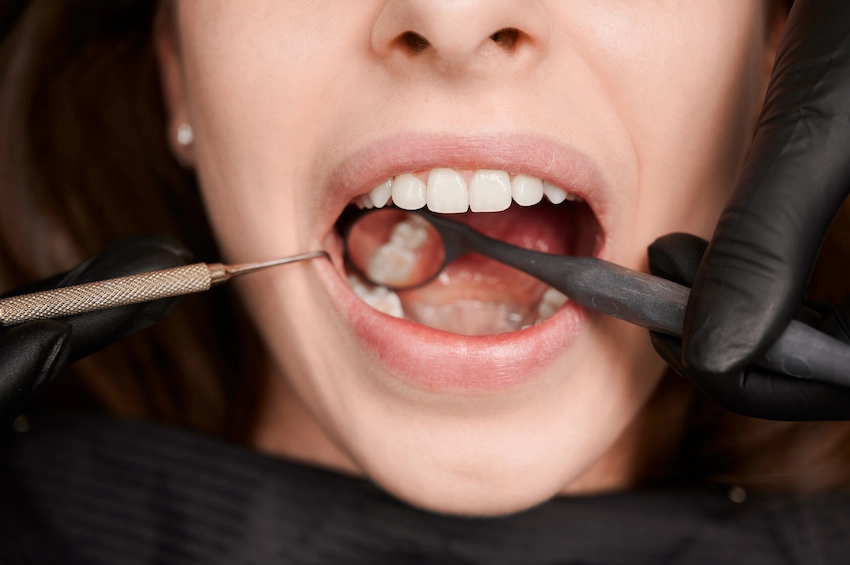
Treatment of a dental cyst generally requires a cut to be excised, mostly the cyst is large or it is causing damage to the teeth that surround it. The cyst is painstakingly removed by the dentist who may also extract any tooth affected that is not vital. In cases where there is a possibility of the tooth getting infected because of the cyst, a root canal treatment may be carried out to avoid the extraction of the tooth. After extraction, the area is typically irrigated and closed with sutures for healing.
If the cyst is tiny and not creating much trouble, a dentist may decide to go the conservative way of monitoring it and cleansing it regularly. Nonetheless, the usual method of getting rid of a dental cyst is through surgery and it has been found to work effectively.
How Serious Are Dental Cysts?
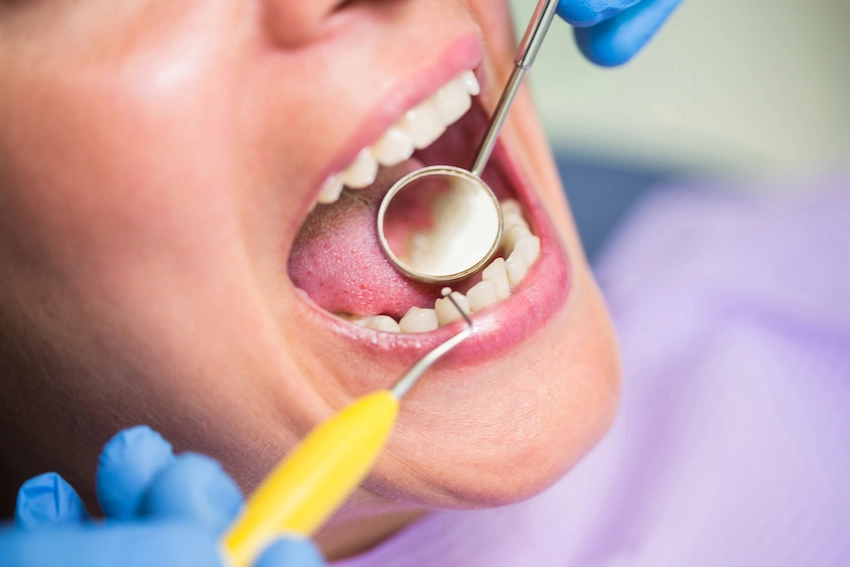
When left untreated, dental cysts lead to significant and several complications, such as the following:
- Infection of surrounding teeth: The cyst may grow in size and place pressure on the teeth close to it, which may result in tooth decay, thinning, or the loss of the tooth.
- Loss of bone: Bigger cysts in the area of the jawbone can lead to a weakening of the jawbone, with a subsequent risk of fracturing.
- Formation of abscesses: In cases of dental cyst infection, the result can be an abscess, which can cause a lot of pain and other oral diseases.
- Tooth misalignment: The pressure from the cyst may create a space between the teeth, thus changing the position of the teeth and causing misalignment.
Immediate treatment of dental cysts would not only stop all the mentioned complications from occurring, but it would also prevent you from dealing with any further damage to your oral health.
Side Effects of Removing a Tooth Cyst
After the removal of a tooth cyst, some people may experience mild swelling and discomfort, for which pain medication is the usual relief. But in specific cases, there might be unexpected problems, such as:
- Wound infection: Infection that appears after tooth surgery is quite rare, but it does happen, mainly due to insufficient and wrong post-operative care.
- Nerve injury: In cases where the cyst was near a nerve, a patient could suffer nerve damage. A mild case may cause a temporary numbness in the affected area, while severe cases could lead to permanent numbness.
- Healing delay: Smoking, poor oral health, or underlying health problems can be some of the things that will slow down the healing process, and, therefore, in some cases, the time between the surgical operation and complete healing will be prolonged.
The correct execution of the aftercare plan your dentist has established is crucial in preventing any of these complications from taking place and ensuring that the wound will actually heal.
Is It Possible to Treat a Dental Cyst without Surgery?
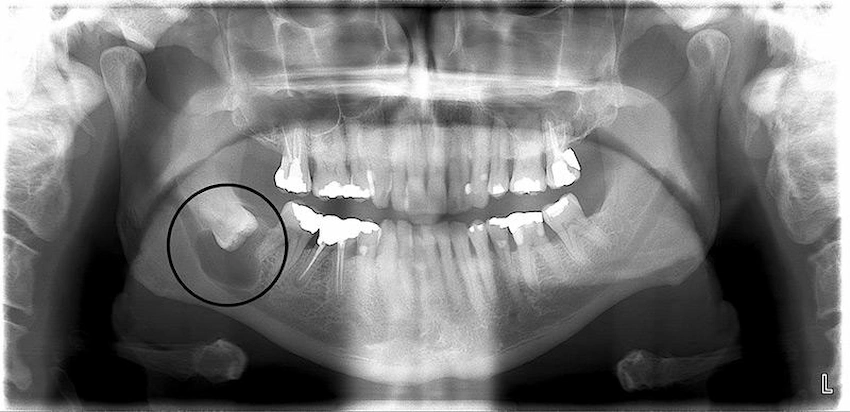
It is feasible to treat small dental cysts that are asymptomatic and do not cause any impairment without surgery in some cases. One such treatment option is:
- Observation: The dentist may advise the patient to keep an eye on the cyst if it is still small and not causing any discomfort. In such a manner, the situation is under control without the need for surgical intervention.
- Medicine: The dentist can proceed in this direction if he/she thinks the cyst has been infected. That is, a person can take antibiotics to chase the bacteria from the cyst before the surgery is carried out.
However, the vast majority of dental cyst cases can only be resolved by surgery, and until the problem is eliminated.
FAQ: How to Treat a Dental Cyst?
Yes, it is indeed dangerous because the contents can leach acid that eats teeth and fills the jawbone which may even cause an infection if unluckily the outer layer of the tooth is eaten off and still no treatment is there. Additionally, it can cause pain and swelling of the gums due to infection.
One way to remove a cyst from a tooth is to perform surgery. Generally, the dentist has other options to deal with the situation. If the cyst is quite large and not in the right place, then your dentist may suggest a root canal or tooth extraction in addition to removal.
Tooth cyst surgery seems not to be a very complicated operation overall, but the complexity will vary since it depends on the size and location of the cyst. With practice, the majority of patients experience no problems can recover quickly, and are also free of pain.
It is sometimes the case, where the dental cysts, which are small and do not show any symptoms are left for a while without being treated or m. Small cysts may be the root of swelling and infection and therefore surgery may be required if the cyst grows or causes any unwanted symptoms.
Once the cyst ruptures, you are at higher risk of developing an infection that may include severe pain and swelling. It is, therefore, important to see a dentist right away to treat the infection and prevent the condition from getting any worse.




